There are many situations where it is desirable to challenge the validity or patentability of a granted patent or pending patent application. For instance, an invalidity search can be useful for an invalidity opinion to mitigate infringement liability, an invalidity defense in litigation, a proactive challenge to patentability at the U.S. Patent & Trademark Office (USPTO), or a pre-issuance submission (observations) to try to restrict or prevent a patent from being issued. But what is the best timing for such an invalidity search?
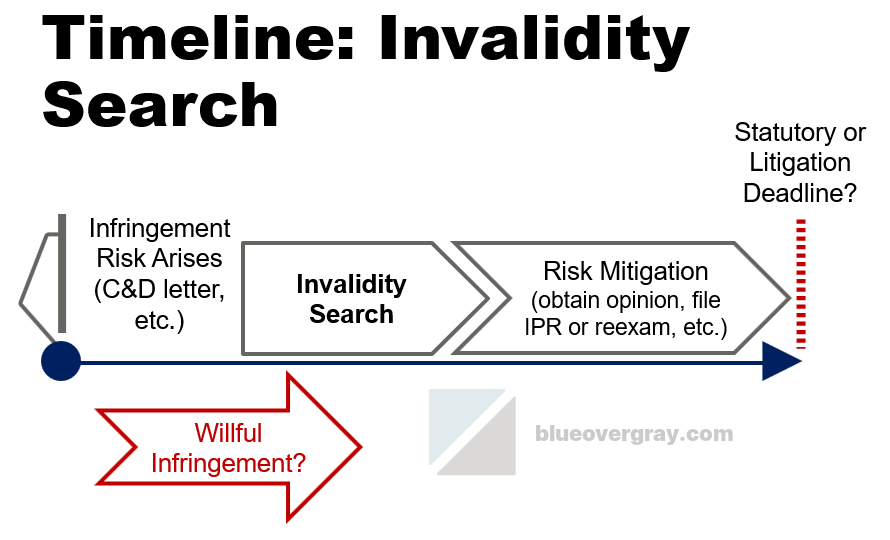
In one sense, an invalidity search is never strictly legally required. Though, practically speaking, invalidity searches are often crucial to avoiding or reducing liability for patent infringement in many contexts. These searches must be performed in a timely manner to obtain the greatest value from them. That includes performing searches in time to meet deadlines that require having suitable search results available.
Patent invalidity searches are reactive in the sense of being conducted in response to some infringement risk arising. That could be the receipt of a cease & desist letter, the filing of an infringement lawsuit against you, or other knowledge of a potentially problematic patent (e.g., via a freedom-to-operate study). In any event, an invalidity search requires first knowing which patent is the subject of the invalidity search. That is because an invalidity search depends on the scope of the particular claim(s) of concern and their effective filing date(s)—including any priority date(s).
It is a best practice to consider an invalidity search after a tangible risk of patent infringement comes to your attention. Knowledge of a patent coupled with a reasonable belief that infringement might be present can potentially give rise to enhanced damages for infringement. And knowledge of a pending patent application can potentially give rise to so-called “provisional rights” to pre-issuance infringement damages.
There may be deadlines that determine when invalidity search results are needed. For instance, in patent litigation in a district court, the court will issue a scheduling order that often sets a deadline to set for invalidity contentions. In is necessary to have search results available in order to formulate those invalidity contentions and prepare a suitable report. Other times, invalidity contentions might be requested through discovery requests, such as interrogatories. Either way, it is crucial to perform the invalidity search far enough in advance of such deadlines to allow for subsequent legal analysis of the search results.
Moreover, there are situations where a proactive challenge to a granted patent is desired. Proceedings such as inter partes review (IPR), post-grant review (PGR), oppositions, and the like may have various different deadlines by which a challenge must be filed. Such deadlines drive the timeline for completing invalidity searching. Just as in litigation, the search must be completed with time to spare to allow for legal analysis and preparation of any formal filing papers for the patent challenge, which may require considerable effort to prepare. Additionally, a pre-issuance submission (or observation) might be filed against a pending patent application and there likewise are both formal and practical deadlines to do so.
Lastly, if an opinion of counsel setting forth grounds for liability is desired to mitigate potential infringement damages, such an opinion should ideally be obtained before your relevant product (or process) is commercially launched. If patent in question is discovered only later, then such an opinion should be obtained without unreasonable delay. Having invalidity search results is a prerequisite to completing an invalidity opinion.
In all these possible settings, it is common for multiple invalidity searches to be performed. That can include follow-on invalidity searches performed in an iterative manner, in order to exhaustively locate prior art and to try to obtain sufficient prior art for desired (and reasonable) invalidity arguments as those arguments evolve and develop. It may also include searches performed by different searchers in different databases (including in non-patent literature databases), in different native languages, though investigation of prior public use and on-sale activities, and the like.
Have an invention you would like to patent? Have a brand you would like to register as a trademark? Concerned about infringing someone else’s intellectual property? Is someone else infringing your IP? Need representation in an IP dispute? Austen is a patent attorney / trademark attorney who can help. These and other IP issues are his area of expertise. Contact Austen today to discuss.
