3 Basic Requirements
In order to get a patent for an invention it must be patentable. There are three basic requirements for patentability:
An applicant gets to define an invention in “claims” of a patent application. Patentability is always analyzed by looking at those claims. If a claims fails any requirements for patentability, then the applicant is not entitled to a patent on it. Though it is still possible to consider the patentability of an invention in an informal sense even before any claims are written. However, judgments about patentability (or validity) can be challenging and subject to dispute.
There are other patentability requirements, such as enablement and definiteness. But these other requirements go more to the form and content of a patent application. You might even say those other requirements are about an application being presented in a patentable form rather than being about the patentability of an underlying invention in the abstract. Only the three basic requirements are discussed below.
Utility
Utility is about the nature of the invention itself. If you write a novel it can never be patented. That is because it is not “useful”. So it fails the utility requirement. But that is an easy example. Nobody thinks of the contents of a book as an invention. So what “useful” inventions are patent-eligible? U.S. patent law states, “Whoever invents or discovers any new and useful process, machine, manufacture, or composition of matter, or any new and useful improvement thereof, may obtain a patent therefor . . . .” Despite that broad definition, laws of nature, natural phenomena, and abstract ideas are not patent-eligible. A claimed invention that is nothing more than one of those things is “preemptive” and fails the utility requirement.
Most man-made inventions have utility. Questions about patent eligibility (utility) tend to arise most for software, methods of medical diagnosis and treatment, biotechnology/life sciences, and business methods. In those areas, the way a patent application and its claims are drafted tends to get a lot of scrutiny.
For design patents, ornamentality is required instead of utility. Ornamentation can be (a) the shape of an article itself, (b) something applied to or embedding in an article, such as surface ornamentation, or (c) a combination of the first two possibilities. Also, the ornamentation must be applied to an “article of manufacture”. A picture standing alone is not eligible for design patent protection. But aside from ornamentality replacing the utility requirement, both of the other patentability requirements (novelty and non-obviousness) still apply to designs.
Novelty
Novelty means that an invention cannot be identical to something already known. For instance, if a claimed invention was already disclosed in someone else’s earlier patent then it lacks novelty. In this respect, assessing novelty involves a comparison that first requires an understanding of what came before. Lack of novelty is commonly referred to as “anticipation”.
However, only certain documents and information can be considered for patentability. Whether or not something qualifies as “prior art” against a given patent claim must first be established. Usually the question is whether a given patent or publication is old enough to be considered prior art. U.S. patent laws set forth somewhat complicated definitions of prior art and novelty. But, in general, earlier patents, printed publications, public uses, and sales can all potentially qualify as prior art. Even inventors’ own past actions and writings can count as prior art against them.
Sometimes novelty is described as “absolute novelty” because inventors are charged with constructive knowledge of all prior art. In other words, it doesn’t matter whether the inventor actually knew about the relevant prior art or not. The novelty requirement bars more than inventions copied from elsewhere. Even obscure disclosures about inventions that are not commercial available—and may never have been—may bar patentability.
Novelty also takes into account inherent teachings. It goes beyond explicit, literal prior art disclosures to further encompass what is unstated but necessarily implied. So, for example, if the prior art structure is the same as what is claimed, then previously unappreciated properties and benefits of that structure are likely inherent even if unstated in an earlier patent.
Novelty and anticipation always refer to what was (explicitly or inherently) disclosed in a single prior art reference. This distinguishes novelty from obviousness, which is discussed below.
Non-Obviousness (or Inventive Step)
Non-obviousness means an invention must represent a significant advance over what was already known in order to be patentable. U.S. patent laws say that even if the claimed invention has novelty, it will not be patentable “if the differences between the claimed invention and the prior art are such that the claimed invention as a whole would have been obvious . . . to a person having ordinary skill in the art to which the claimed invention pertains.” Many other countries use the term “inventive step” to refer to the concept of non-obviousness.
Obviousness is formally analyzed by first determining the scope and content of the prior art, the differences between the prior art and the claim at issue, and the level of ordinary skill in the relevant art. Those facts must be taken into account when drawing a legal conclusion about obviousness or non-obviousness. So-called secondary considerations for non-obviousness can also be considered. But such secondary evidence is often not available.
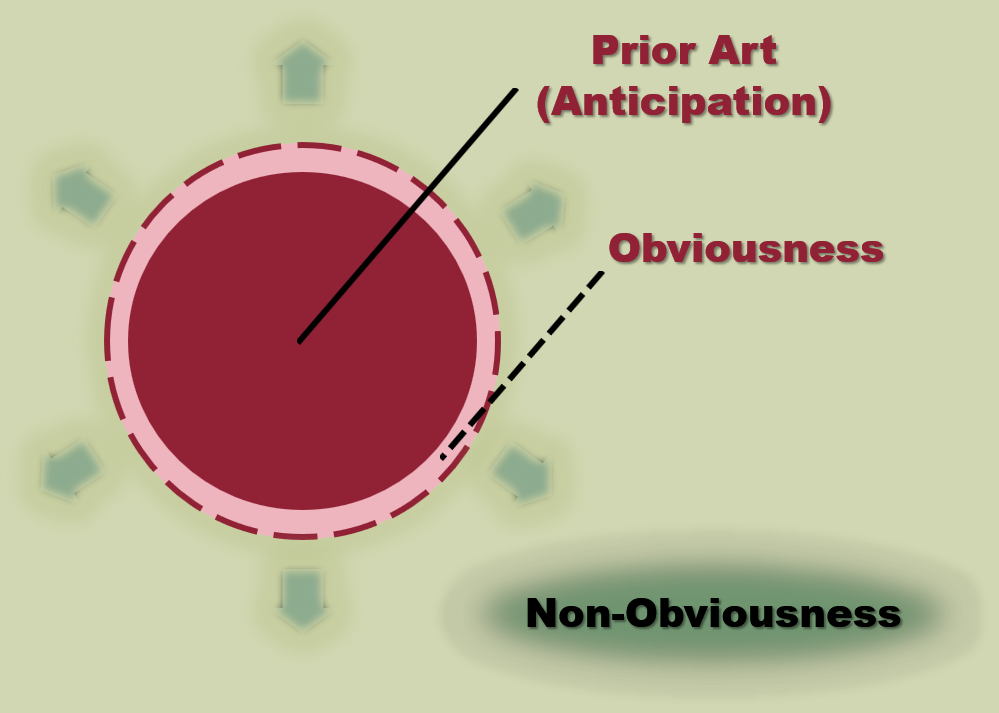
It is possible to conceptualize obviousness as a fuzzy zone around the closest prior art. In that zone the invention is too trivial to be patentable. An invention must go far enough beyond the prior art to be worthy of a patent. Though exactly how far is hard to establish with a bright line. The main way to reach non-obviousness is to claim something that solves a technical problem in the prior art. You do need an invention and cannot merely claim the absence of the prior art or the absence of a problem. After all, patentability is about encouraging inventions that positively contribute to human knowledge. That is how this ties in to the reason patents exist.
In practical terms, patent application claims are often rejected by an examiner for obviousness based on a combination of multiple prior art patents. In those situations, no single earlier patent discloses all the features or elements of a given patent claim. But the examiner can assert that someone would have been motivated to combine or modify the different teachings of multiple earlier patents to arrive at the claimed invention (with a reasonable chance of success). These are often difficult judgments to make. And there can be a temptation to slide into hindsight bias. These are some of the reasons why obviousness is sometimes called the ultimate condition for patentability.
Have an invention you would like to patent? Have a brand you would like to register as a trademark? Concerned about infringing someone else’s intellectual property? Is someone else infringing your IP? Need representation in an IP dispute? Austen is a patent attorney / trademark attorney who can help. These and other IP issues are his area of expertise. Contact Austen today to discuss.
